研究1:Outcomes in Reoperated Low-Grade Gliomas
标题:低级别神经胶质瘤二次手术的效果
BACKGROUND:Low-grade gliomas(LGGs)comprise a diverse set of intrinsic brain tumors that correlate strongly with survival.Data on the effect of reoperation are sparse.
背景:低级别神经胶质瘤包括了一系列的与之生存率密切相关的颅内肿瘤。关于二次手术效果的数据却很少。
OBJECTIVE:To evaluate the effect of reoperation on patients with LGG.
目的:评价低级别神经胶质瘤(LGG)患者二次手术的效果。
METHODS:Fifty-two consecutive patients with reoperated LGGs treated at the University of Washington between 1986 and 2004 were identified and evaluated in a retrospective analysis.
方法:1986年至2004年在华盛顿大学接受二次手术的连续52名LGG患者被纳入本次回顾性研究分析。
RESULTS:The average overall survival(OS)for this cohort was 12.95±0.96 years.The overall 10-year survival rate was 57%.The absence of any residual tumor at either the first or second operation was associated with significantly increased OS.Negative prognostic variables for OS included the use of upfront radiation and pathology at recurrence.The average overall progression-free survival to the first recurrence(PFS1)was 6.23±0.51 years.Positive prognostic factors for improved PFS1 included the use of upfront radiation therapy.Variables not associated with differences in PFS1 included the use of upfront chemotherapy,enhancement,pathology,extent of resection,the presence of residual tumor,and Karnofsky Performance Scale score<80.The average overall progression-free survival to the second recurrence was 2.73±0.39 years.Pathology at recurrence was associated with significant differences in progression-free survival to the second recurrence,as was extent of resection at time of first recurrence,and Karnofsky Performance Scale score<80.
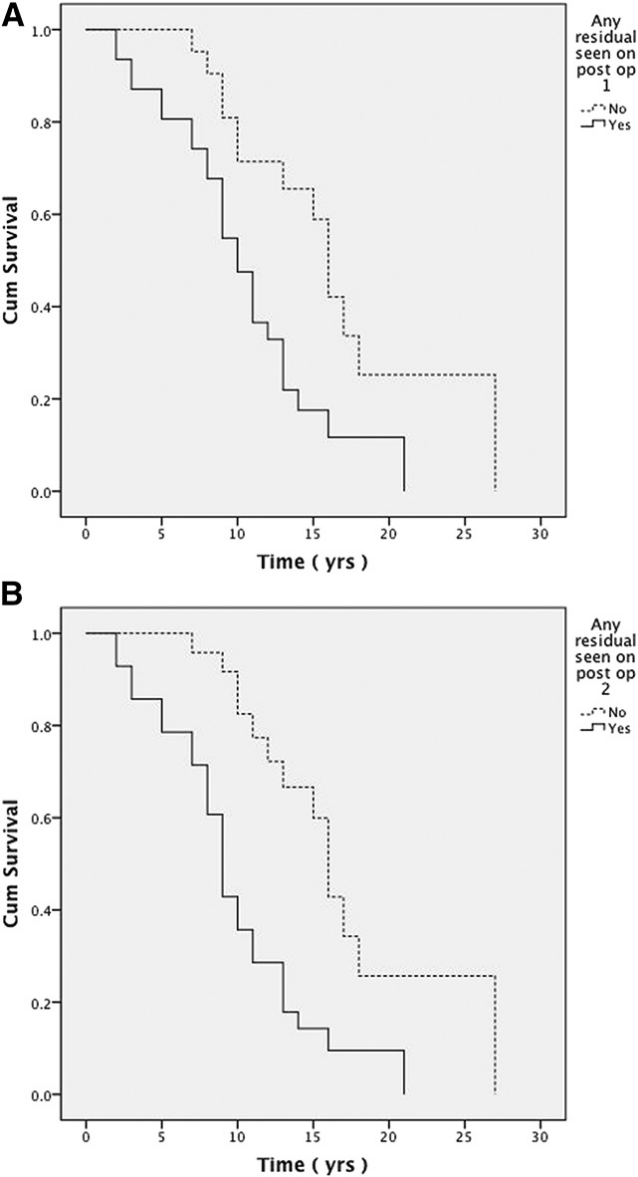

A,一次手术后任何残留物的存在表明对总存活率有的不利影响(OS;16.7 1.8 vs 10.5 1.0年;P=.004).
B,复发和再次切除后任何残余物的存在表明对OS有的不利影响(17.2±1.7对9.8±0.9年;P%3C.001)。
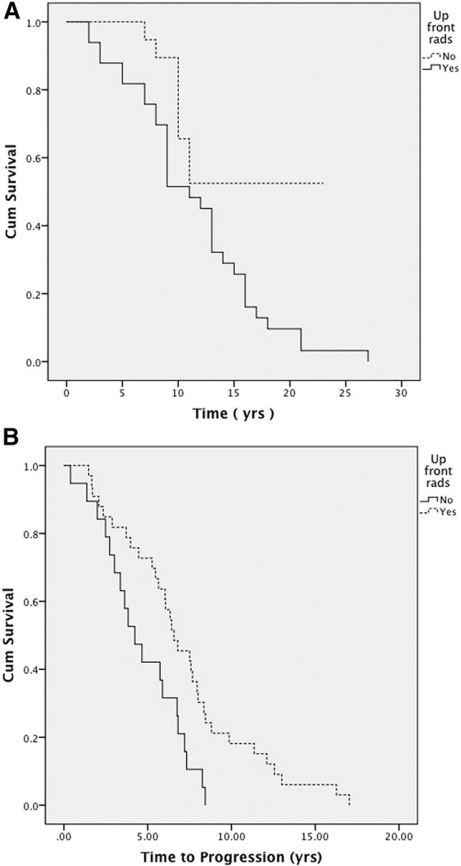

A,前期放疗与恶化的总生存率相关(16.6±1.6比11.4±1.0年;P=.03).
B,前期放疗与一次复发的无进展生存期相关(4.64±0.5比7.2±0.7;P=.007).
结果:本组患者的平均总生存时长为12.95±0.96年。10年生存率57%。肿瘤切除干净与一次或二次手术后总生存时长(OS)明显增加相关。OS阴性预后变量包括前期放疗和病理提示肿瘤复发。到一开始复发前的平均无进展生存期(PFS1)为6.23±0.51。提高PFS1的因素包括前期放疗。与PFS1差异无关的变量包括前期放疗的使用,强化,肿瘤病理分型、手术切除范围、肿瘤残余以及卡氏评分<80分。二次复发的无进展生存期平均为2.73±0.39年。二次复发前的无进展生存期差异与复发的肿瘤病理类型、一次复发的切除范围和卡氏评分<80分明显相关。
CONCLUSION:This is among the largest studies to assess variables associated with outcome in patients with reoperated LGG.Reresection appears to provide significant benefit,and extent of resection remains the strongest predictor of OS.
结论:这是评估LGG患者二次手术预后相关变量的较大研究之一。二次手术似乎有明显的效果,手术切除的范围仍然是OS的较强评估因素。
研究2:Impact of repeated operations for progressive low-grade gliomas
标题:反复手术对进展性低级别胶质瘤的影响
Background:Maximal,aggressive resection of diffuse low-grade gliomas(DLGG)is well established as the standard of care in neuro-oncology.The role of repeat resection for tumor progression is unclear.
背景:弥漫性低级别胶质瘤(DLGG)的较大、侵袭性切除已被确立为神经肿瘤的护理标准。重复切除对肿瘤进展的作用尚不清楚。
Objective:To assess the role of repeated operation for DLGG,and the effect on malignant transformation and survival.
目的:探讨DLGG反复手术对其恶性转化和生存的影响。
Methods:We conducted a historical cohort study in which all patients undergoing multiple resections of DLGG between the years 1995-2019 were evaluated for overall survival(OS)and time to transformation(TTT).We then compared the outcome of this group with that of a matched control group comprised of patients who underwent only one operation despite being eligible for repeat surgery at tumor progression,but had received non-surgical oncological therapy or declined additional treatment.
方法:我们进行了一项历史队列研究,评估了1995-2019年期间全部多次切除DLGG的患者的总生存期(OS)和转化时间(TTT)。然后,我们将这一组的结果与一组匹配的对照组的结果进行了比较。对照组的患者在肿瘤进展时虽然有资格再次手术,但只接受了一次手术,但接受了非手术肿瘤治疗或拒绝了额外的治疗。
Results:Of 607 patients in our departmental DLGG database,93 patients underwent 2 or more surgeries and had sufficient follow-up and imaging data to be included in the study group.Thirty-eight patients were included in the matched control group.Early(less than 1 year)progression was associated with decreased survival and shorter TTT in the study group.Patients undergoing multiple resections had significantly longer TTT and OS compared to patients who underwent a single surgery.This effect was especially noted in patients who had radiological evidence of tumor transformation.
结果:在我科DLGG数据库的607例患者中,有93例患者接受了2次或2次以上的手术,并有足够的随访和影像学资料纳入研究组。38例患者被纳入匹配的对照组。在研究组中,早期(小于1年)进展与生存率降低和TTT缩短相关。与只接受一次手术的患者相比,接受多次手术的患者的TTT和OS明显更长。这种效应在有放射学证据的肿瘤转化的患者中明显。
Conclusions:Repeated resections of LGG are safe and offer survival benefit in select patients.Early progression following resection is associated with worse prognosis.Patients with evidence of radiological transformation may benefit the most from re-resection.
结论:反复切除LGG是顺利的,并在特定的患者中提供生存优势。切除后早期进展与预后较差相关。有放射学转变证据的患者可以从再次切除中获益较大。




